
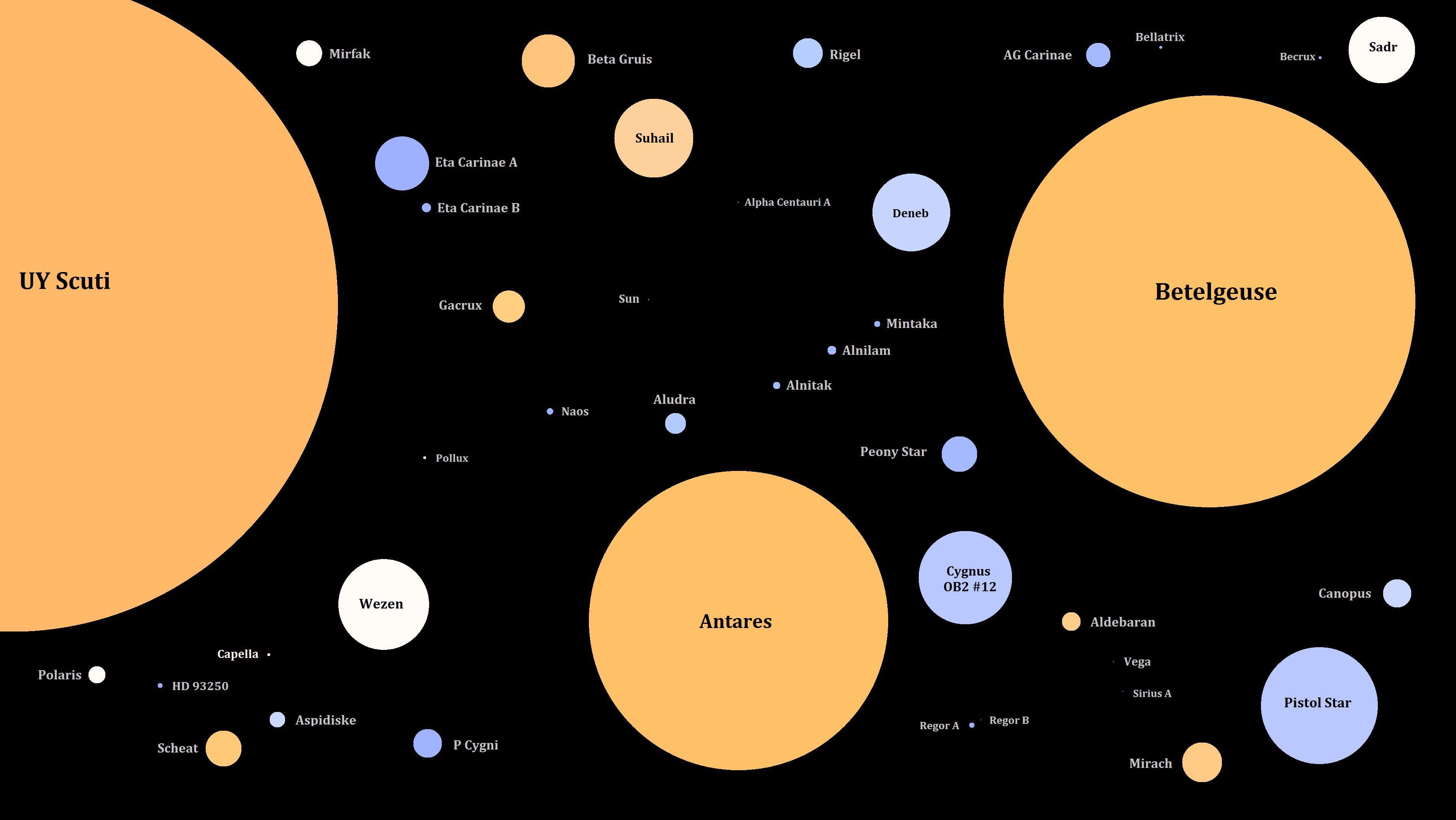
[Image source: wikimedia.org under Creative Commons License and Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International ]
When we look up into the night sky, we see lots and lots of stars. They are very hard to define when you keep looking at them. You can't tell how big or small they are.
A star is a space object, which uses nuclear fusion as is fuel. It is a ball of fire and gas compressed by its strong gravity. When star starts to die it turns into huge red giants and turns into white dwarf. High mass star such as A type stars or red super giants or hypergiants blow up into huge supernova or a neutron star or a pulsar. B type are very different. The high mass B type star and O type stars blow up into huge black hole; so each type of star has a different type of level. Stars can be understood using G2V. G stands for the classification of stars while the V stands for luminosity. If they are lower mass B type star they can blow up into a neutron star or a pulsar which is a very dense type of star. Binary or multi star system if they are 2 or more stars than they can go to stable orbit until they die. However most of the star in the universe including all stars outside our galaxy the Milky Way are invisible to the naked eye from Earth. Indeed some stars are invisible from Earth even from the most powerful telescope. They will be lots of important facts about stars. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun.
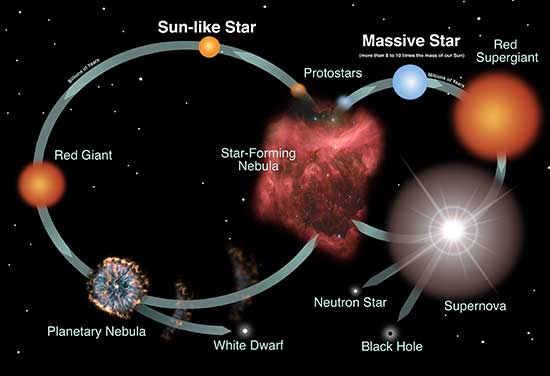
In every single star in the universe has the same beginning, but different ending. This is how star is born; it starts from a cloud full of dense material, the more dense it is the more massive it will be. The cloud will start spinning until it gets compressed and it will blow up into a star, which goes through nuclear fusion and this state is now a protostar. A protostar is the beginning stages of a star from then on it will keep on going nuclear fusion until they run out of fuel. Our Sun is combining every single day lots and lots of hydrogen into helium. It will go through this process for about 5 billion years until it runs out of hydrogen and it is only helium. Gravity is trying to crush it but it can go through nuclear fusion with helium which can make heavy element such as oxygen and carbon and it will balloon up into a red giant and it will swallow up most of the whole inner solar system. From there it will loose its outer layers turning into a very dense white dwarf. These type of deaths are only found in M,K,G and F type of stars.
Red supergiants have 8 types of stars. Red hypergiants and low mass B type stars can explode into a neutron or pulsar star. It will go into a red supergiant and goes through supernova, which can go into a neutron star. In higher B type and O type stars it can balloon up into a red supergiant until it turns into black hole. Wolf Rayet star can blow up into a supernova with a huge gamma ray burst. Gamma rays are part of the electromagnetic spectrum. The spectrum includes: radio waves, microwaves, infrared waves, visible light, ultraviolet rays, x-rays, and gamma rays.
[Image source: nasa.gov]
When a star reaches around 8 or more solar masses, the star will end its life in a bang which is also known as a supernova. There are two main types of supernovas. There is the Type 1 supernova and Type 2 supernova. The Type 1 supernova is rarer as this happens with a white dwarf and some other type of star. One very famous example is the Sirius system. It contains an A-class star called Sirius A and a white dwarf called Sirius B. During a Type 1 supernova the white dwarf starts stealing material from its companion star which slowly increases its mass and once it reaches the Chandrasekhar Limit(1.44 solar masses) it erupts and explodes in a fraction of a second. This can be seen in the night sky by the naked eye.
Type 2 supernova happens within the star. Unlike the Sun, higher mass stars are able to fuse heavier elements. When the star slowly fuses all the hydrogen there is left, it starts fusing heavier elements in the following order(including hydrogen): hydrogen, helium, carbon, neon, oxygen, magnesium, silicon, and iron. Once the star fuses the silicon into iron, the iron core can`t fuse into more heavier elements as it would take more energy than the star can produce, so the the core collapses into itself creating a neutron star or a black hole. This can also be seen in the night sky with the naked eye.
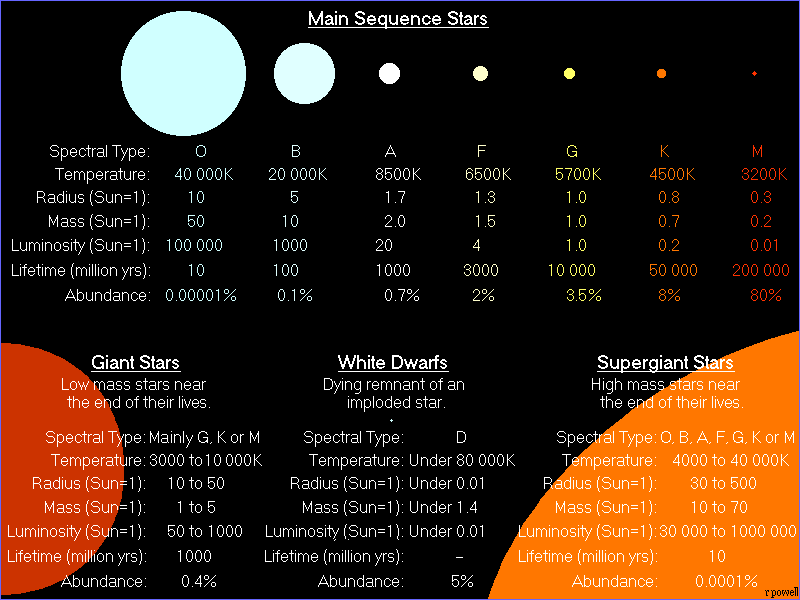
[Image source: atlasoftheuniverse.com under license]
Have you ever heard about a brown dwarf ? Brown dwarves look very similar to gas giants, but they are failed stars. Every single star have to go through a process called nuclear fusion. This is where atoms are crushed to form a different type of atom. Brown dwarfs can't go through nuclear fusion, so they act like huge and very massive gas giants. There are classifications of brown dwarfs : L, T, and Y.

[Image source: nasa.gov]
These types of brown dwarfs have the highest temperature range 1300 kelvin to 2000 kelvin other than the brown dwarfs. They are also the most massive brown dwarfs. These type of brown dwarfs have very little light. One example of an L-type brown dwarf is GD 165b rotates around a while dwarf which is a star which is very dense and small as the Earth.
Class T type brown dwarf which cooler are less masses than the L class brown dwarf . These typeof brown dwarf have a temperature about 1300 kelvin to 700 kelvin.
One example of T class is Gliese 229B which rotates around a red dwarf star.
These type of Y-class brown dwarfs are not well defined. They are like a brown dwarf and a gas giant. One example is CFBDSJ 005910.90-011401.3. They are expected to be much cooler than T- dwarfs.
M class stars are known as red dwarfs. They are the most common type of stars in the whole universe. So 85% of star in the Milky Way are just red dwarfs. The closest star to us is called Proxima Centauri and it is a red dwarf. A red dwarf can stay longer that any other star not including brown dwarf. They have very low mass which is around half of the mass of the Sun. Red dwarfs are also known to support planets which can have life. Many red dwarfs are part of binary systems. One example of multiple star system which include red dwarfs is called the Castor system which includes 6 stars. They can be huge red giants and one of the most famous Betelgeuse. The largest star ever discovered is a variable star called UY Scuti. It is not a red hypergiant since its mass is very low. A variable star is a type of star which can change its luminosity and size.
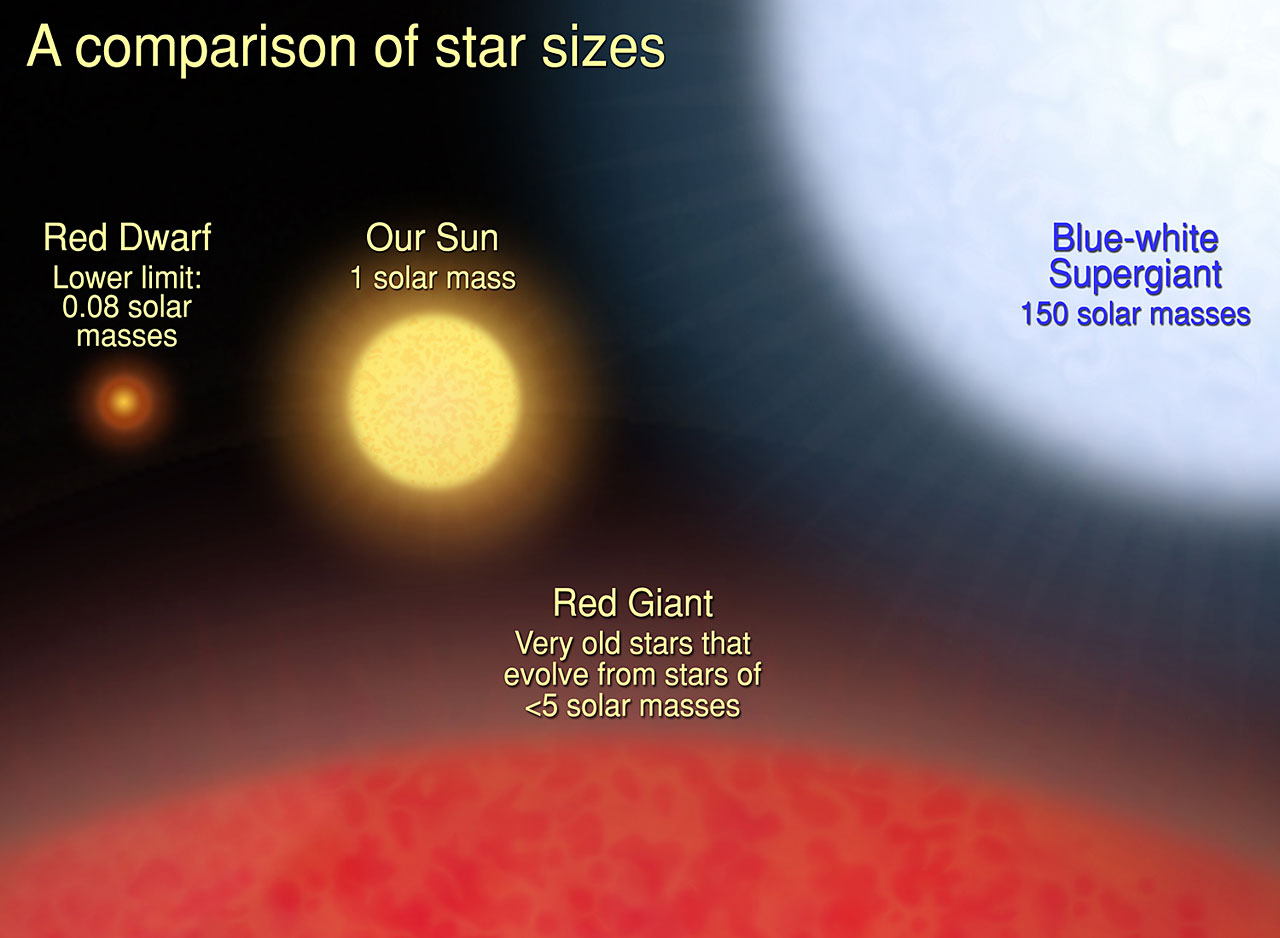
[Image source: nasa.gov]
K class stars are more massive than red dwarfs, but less massive than our Sun. There temperature is from 3,900 kelvin to 5,200 kelvin. There are also known as orange dwarfs. They 80 % of the mass of the Sun. They have a long lifespan for about 15 to 30 billion years. They have planets which may support life. This type of stars are a little bit smaller than our Sun. There can also be orange giants and one famous orange giant is a star called Arcturus. Orange giants are bigger in size and more massive than our Sun although K type star, an example is Arcturus.
[Image source: wikimedia.org under Creative Commons License ]
G class stars are known as yellow dwarfs. The most famous G type star is the Sun. These type of star have the mass about 0.8 to 1.2 masses of the Sun. There is something called a yellow supergiant which can be A, G or F type star. One example W Virginis.

[Image source: nasa.gov]
F class stars are yellow-white dwarfs. They have a temperature between 6000 kelvin to 7600 kelvin. They have a lifespan about 4.3 billion years. In the whole galaxy there is 2% of F type stars. One example of F type star is Tau Bootis-A.
An A type star is also known as blue dwarf star. It has a temperature 7,600 K to 11,500 K. These type of star has 1.6 solar masses (masses of the Sun) to 2.4 solar masses.
A type star looks like white bluish type of star. Some A type star can be binary star such as the Sirius system which is made up from an A type star (Sirius A ) and a white dwarf ( Sirius B ). A type of star has a very short lifespan for about few million years. There is about 0.7% A type star in the whole galaxy. One of the most famous stars is Sirius.
These type stars have 2 to 16 times mass of the Sun. These type of stars have a temperature about 10,000 kelvin to 30,000 kelvin. This is bluish type of star. Very few B type stars have planets. There type of star can easily found in the night sky because they are so luminous. Some B type stars be part of multiple star system such as the Rigel System. This includes 3 stars Rigel A, Rigel B, Rigel C. They have a lifespan for about 10 million years.
O type of stars are very very rare. These type of stars in the whole galaxy are .00003%. When they explode the results is a black hole surrounding with planetary nebula. Many of these stars are blue super giant or hypergiant which is a type of a star which is very huge. There are 20,000 O type stars in the whole galaxy. The mass of these stars are 15 to 90 times the mass of the Sun. The temperature is between 30,000 K to 52,000 K. These type of stars don't have any planet since it can rip them apart even when they are young.
These type of stars have temperature about 30,000 kelvin to 200,000 kelvin. These type of wolf rayet stars have different classes . There is WN star which releases nitrogen and oxygen. There is WC star which releases carbon and oxygen. There is WO star which releases mostly oxygen. The most massive star ever discovered is called R136a1, which is located in the large magellanic cloud which is our neighbouring galaxy and it is also wolf rayet star.
Neutron stars and pulsar are one of the most dense objects in the whole universe. A neutron star is the collapsed core of a large star which had 10-29 solar masses. They have a radius about 11 to 11.5 km (almost the length of Manhattan), but they have a mass about 2 times the mass of the Sun. When a neutron star rotates rapidly it will release electromagnetic radiation beams like X-rays, UV-rays, it will now become a pulsar.
A star which has the mass which is greater than 8 times the mass of the Sun can become a neutron star when it blows up. Once the star blows up, it will make a very dense core is made up of neutrons. Neutron is like a glue for the protons to stick together. If you want to pass a neutron stars you would need to go about one hundred thousand to about one hundred fifty thousand km/s. Another way of creating neutron star is where the star explodes into a Type A supernova. Once the remnant is the neutron, and if the remnant is five times greater than the Sun than it will become a black hole. A neutron star starts rotating rapidly and starts to release beams of electromagnetic radiation and ends up being a pulsar.
A neutron star has 1 to 3 solar masses. The maximum ever observed mass of a neutron star is about 2.01 solar masses. The temperature of a neutron star is about is about 10 to the power of 11 K to about 10 to the power of 12 K.
If you had a teaspoon of a neutron star it would weigh more than Mount Everest.
Neutron stars have very strong magnetic field. Neutron stars have a range of 10 to the power of 8 to 10 to the power of 15 Gauss and 10 to the power of 4 to 10 to the power of 11 Tesla. Gauss and Tesla are a measurement of the magnetic field. If a neutron or a pulsar have very strong magnetic fields than they can become magnetar.
The gravity of a neutron star is about 2 * 10 to the power of 11 times stronger than Earth which is about 1.86 * 10 to the power of 12. If you stand on a neutron star you will be flattened. A neutron star can create a tiny gravitational lensing effect since it is so dense.
In the pulsar and neutron star has a structure like other stars. In the outer crust it is made up of ions and electrons. Ions are charged atoms like positive and negative. One example is salt. It is made up of positive sodium atom and a negative chlorine atom. 1km to 2km under the surface is the inner crust. The outer core is about 9 km under the surface of the neutron or pulsar star. The pressure is about 0.5 to 2 Pa ( Pascal ). It is made of neutron and protons and fermi liquid and 3% electron fermi gas.

[Image source: wikipedia.org under Creative Commons License and Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International ]
Neutron stars release electromagnetic radiation, but neutron star can pulse radio waves which that can become a pulsar. Pulsars are known to give out infrared rays, visible light, ultraviolet rays, X-rays, and gamma rays. Pulsars that give out X-rays are called X-ray pulsars. One famous X-ray pulsar is the Crab pulsar located in the Crab Nebula.
Neutron stars slow down their rotation just like the Earth which is slowing down. When the neutron stars are slowing down, it is called spin down. When the neutron star starts to speed up it is called spin up.
Glitches is where the neutron star's rotation increases in speed or spin up. Starquakes are when the neutron star's crust ruptures and creates a starquake. If a star quake happens on a magnetar it will create gamma rays. There is something called an anti-glitch. This is a type of glitch where the rotation of the neutron star speeds up or speeds down.

[Image source: nasa.gov]
Binary neutron stars and pulsars are rare. One is Hulse-Taylor. Hulse is a pulsar while Taylor is a neutron star. One other system is the Black Widow pulsar, this system includes a pulsar and a brown dwarf. A brown dwarf is a failed star. The pulsar is eating the brown dwarf. When it is a neutron binary there is a chance of a collision and the result will be a black hole.

[Image source: nasa.gov]
Neutron stars and pulsars are really amazing. Neutron stars and pulsars are one of the most dense objects in space. They are really small like around 7 or 8 miles. Astronomers can't really find that much. They can find pulsars since they blink when you look at it. Neutron stars have a very dense core which will crush you into to pieces or flatten you. Neutron stars may contain strange matter. Strange matter is a type of matter which acts really strange. Neutron and pulsar stars have planets. Many pulsars have planets called pulsar planets. One example is the pulsar named PSR B1257+12. It has three extrasolar planets rotating around it. Pulsars and neutron star are amazing, so which one is your favorite?
When you look up to sky you will see lots and lots beautiful stars but some stars can be deadly and some stars can be friendly. The classes of stars M,K,G,F,A,B,O and Wolf Rayet Stars and Brown Dwarfs are all unique. The M type star has unique feature for living over trillions of years and has planets which may support life. The K type star is also has planets which may support life and it can support life because it is less harmful than our Sun because it releases less UV rays and lives more longer than our Sun. G type of stars are unique because they are perfect for planets like Earth to support life. F type star are unique because they are very rare. It A type of stars are unique because it can be many times the size of our Sun and it is also very massive. B type stars are unique because their size and mass and luminosity is so much. O type stars are unique because of how rare they are. Wolf Rayet stars are smaller than O type of star but they are more rare, massive, and they are more luminous. Brown dwarfs can stay how long they want and they are almost just like planets except that they are more massive and they are much bigger. One of the stars has a planet which can support life and can be our future planet. So what is your favorite star out of stars in the whole night sky?

[Image source: wikipedia.org]